CFA Level 1 - Assets
Classification of Natural Resource Assets
Intangible assets are identifiable non-monetary resources that have no physical substance but provide the company controlling them with a benefit. Intangible assets can be internally created or acquired from a third party. If intangible assets are acquired in an arm's length transaction, their recognition and measurement will be similar to those of tangible assets. Internally developed intangible assets are accounted for in a wide range of ways. Intangible assets include research and development costs, patents, trademarks and goodwill. Intangible assets are depreciated over their estimated life and they are done so by the use the straight-line depreciation method. Intangible assets cannot have an estimated life of more then 40 years.
Unlike other intangible assets, goodwill is no longer an asset that can be depreciated. As of July 2001, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) adopted the Statement of Financial Accounting Standards (SFAS) No. 142, Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets, which sets new rules for goodwill accounting. SFAS 142 eliminates goodwill amortization and instead requires companies to identify reporting units and perform goodwill impairment tests.
Example
Unlike other intangible assets, goodwill is no longer an asset that can be depreciated. As of July 2001, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) adopted the Statement of Financial Accounting Standards (SFAS) No. 142, Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets, which sets new rules for goodwill accounting. SFAS 142 eliminates goodwill amortization and instead requires companies to identify reporting units and perform goodwill impairment tests.
Example
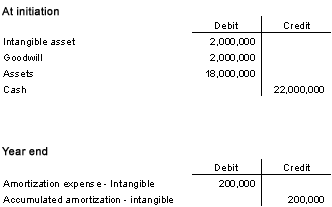
Company ABC acquires a company for $20m. The acquired company's fair market value was $18m. ABC has also acquired a patent for $2m that has an estimated remaining life of 10 years.
Journal entries:
 |






0 comments:
Post a Comment