CFA Level 1 - Equity Investments
With respect to global industry analysis, there are many key elements related to return expectations.
1.Demand analysis
2.Value Creation
3.Industry life cycle
4.Competition
Demand
To begin with global industry analysis, an estimation of demand is needed. This could also include an analysis of substitutes for the company's product. In this context, demand analysis is based on worldwide demand.
Value Creation
This element focuses on the sources of value that can be extracted through the value chain. The value chain consists of suppliers of raw materials, but also the delivery firms that deliver the finished product to the consumers.
Industry Life Cycle
Analyzing the industry life cycle in a global context is important much like it is in domestic industry analysis. It is important to understand an industry's growth prospects to determine an appropriate growth rate.
Competition
Competition in a global industry is much more complicated as the analysis is done with global industries and laws in mind.
The industry life cycle is made up of the following stages:
- Pioneering Phase
- Growth Phase
- Mature Growth Phase
- Stabilization/Maturity Phase
- Deceleration/Decline Phase
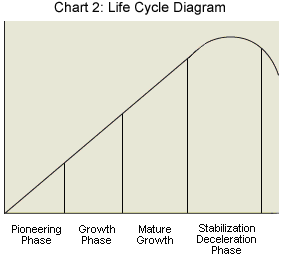 |
1)Pioneering Phase
This phase is characterized by low demand for the industry's product and large upstart costs. Industries in this phase are typically start-up firms, with large upfront costs and few sales.
2) Growth Phase
After the pioneering phase, an industry can transfer into the growth phase. The growth phase is characterized by little competition and accelerated sales. Industries in this phase have typically survived the pioneering phase and are beginning to recognize sales growth.
3) Mature Growth Phase
After the growth phase, an industry will reach the mature growth phase. The mature growth phase is characterized above average growth, but no longer accelerating growth. Industries in this phase now face increasing competition and, as a result, profit margins begin to erode.
4) Stabilization/Maturity Phase
After the growth phases, an industry will enter in the stabilization/maturity phase. The stabilization/maturity phase is characterized by growth that is now average. Industries in this phase have significant competition and the return on equity is now more normalized. This is typically the longest phase an industry will go through.
5) Deceleration/Decline Phase
The deceleration follows the growth and maturity phases. The deceleration/decline phase is characterized by declining growth as demand shifts to other substitute (new) products.







0 comments:
Post a Comment