CFA Level 1 - Liabilities
Recording and Reporting Estimated and Contingent LiabilitiesLiabilities whose timing and amount are known can easily be accounted for. But others - such as warranties, taxes, vacation-pay liability and contingent liabilities, among others - require some estimation.
WarrantiesWhen a company sells a product, it sometimes offers its customers a warranty of a certain number of years. To be consistent with the matching principle, companies, at the time of the sale, must estimate an amount that must be allocated to the costs associated with the warranties. Most companies will use a historical or industry average to estimate its warranty cost. The estimated warranty cost or liability will be allocated to the estimated warranty liability. For example, say Company ABC sells 100 appliances at $100 and estimates that each appliance will carry a $10 warranty liability.
Journal entry:
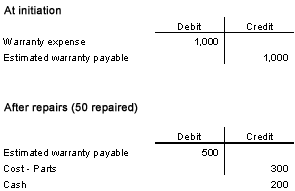 |
TaxesDue to timing differences, companies will report deferred income tax liabilities. These are taxes that have not yet been paid but are expected to be paid in the future. For example, say Company ABC estimates its tax bill will total $500. At year-end it has an actual tax bill of $600.
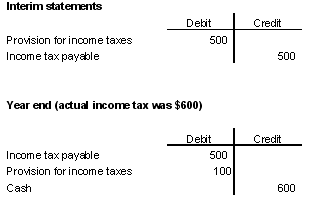 |
Vacation-pay LiabilityThis liability arises when employees do not take their vacation during an accounting period. Even though they have not taken their vacation, they are still entitled to them, and the result is a future liability.
For example, say an executive has three weeks of earned but unfulfilled vacation days, which have a total value to $10,000.
 |
Contingent Liabilities
Contingent liabilities are liabilities that will materialize if some future event occurs and are contingent on a specific outcome. The most frequent contingent liability is a pending lawsuit against the company, which will materialize only if the firm is found guilty. Pending lawsuits can be significantly large for some companies, especially those involved in large class action lawsuits with hundreds or even thousands of potential plaintiffs. Examples of these industries include pharmaceuticals, oil companies or any company that produces large amounts of products that can harm consumers.
The disclosure and/or inclusion of contingent liabilities in a company's financial statements will depend on the company's ability to estimate the amount of the liability and the likelihood that it will occur.
Rules for classifying liabilities:
- If the liability is probable and can be reasonably estimated, it must be included in the company's financial statements. The loss will be included in the financial statements, and the liability must be included on the balance sheet.
- If the liability is probable but cannot be reasonably estimated, then only a footnote disclosure is required.
- If the liability is not probable and cannot be reasonably estimated, then no disclosure is required.






0 comments:
Post a Comment